As a Technician, it is advisable that one must possess a basic knowledge of whatever technology one wishes to work in. Before pr...
As a Technician, it is advisable that one must possess a
basic knowledge of whatever technology one wishes to work in.
Before proceeding any further, let’s briefly try to garner a little knowledge about how a cell phone works?
Have you ever wondered how a cell phone works? What makes it different from a regular phone? What is inside it, or how they made it? What terms like PCS, GSM, CDMA and TDMA mean?
Before proceeding any further, let’s briefly try to garner a little knowledge about how a cell phone works?
Have you ever wondered how a cell phone works? What makes it different from a regular phone? What is inside it, or how they made it? What terms like PCS, GSM, CDMA and TDMA mean?
Want to watch video instead of reading it here?
Please click the Button below
One of the most interesting things about a cell phone is that it is actually a radio - an extremely sophisticated radio. The telephone was invented by Alexander Graham Bell in 1876, and wireless communication can trace its roots to the invention of the radio by Nikolai Tesla in the 1880s (formally presented in 1894 by a young Italian named Guglielmo Marconi). It was only natural that these two great technologies – the telephone and the radio - would eventually be combined into a single device.
If you wish to acquire a deep knowledge in wireless communication, please click the link and learn some Fundamentals of Wireless Communication.
As an entry level technician you just need to have a simple understanding about cell phones.
Below is just some basic information trying to explain some rudimentary concepts
Cell Phone Network Technologies:
2G
Technology
There are three common technologies
used by 2G cell-phone networks for transmitting information:
* Frequency division multiple access (FDMA)
* Frequency division multiple access (FDMA)
* Time
division multiple access (TDMA)
* Code
division multiple access (CDMA)
Although these technologies sound very intimidating, you can get a good sense of how they work just by breaking down the title of each one.
The first word tells you what the access method is. The second word tells us that it splits calls based on that access method.
* FDMA puts each call on a separate frequency.
* TDMA assigns each call a certain portion of time on a designated frequency.
* CDMA gives a unique code to each call and spreads it over the available frequencies.
The last part of each name – ‘multiple access’ simply means that more than one user can utilize each cell.
FDMA
FDMA separates the spectrum into distinct voice channels by
splitting it into uniform chunks of bandwidth. To better understand FDMA, think
of radio stations: Each station sends its signal at a different frequency
within the available band. FDMA is used mainly for analog transmissions. While
it is certainly capable of carrying digital information, FDMA is not considered
to be an efficient method for digital transmission.
In FDMA, each phone uses a different frequency.
In FDMA, each phone uses a different frequency.
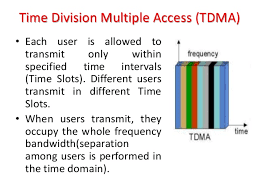
TDMA
TDMA is the access method used by the Electronics Industry
Alliance and the Telecommunications Industry Association for Interim Standard
54 (IS-54) and Interim Standard 136 (IS-136). Using TDMA, a narrow band that is
30 kHz wide and 6.7 milliseconds long is split time-wise into three time slots.
Narrow band means "channels" in the traditional sense. Each conversation gets the radio for one-third of the time. This is possible because voice data that has been converted to digital information is compressed so that it takes up significantly less transmission space. Therefore, TDMA has three times the capacity of an analog system using the same number of channels. TDMA systems operate in either the 800-MHz (IS-54) or 1900-MHz (IS-136) frequency bands.
TDMA splits a frequency into time slots.
GSM
Narrow band means "channels" in the traditional sense. Each conversation gets the radio for one-third of the time. This is possible because voice data that has been converted to digital information is compressed so that it takes up significantly less transmission space. Therefore, TDMA has three times the capacity of an analog system using the same number of channels. TDMA systems operate in either the 800-MHz (IS-54) or 1900-MHz (IS-136) frequency bands.
TDMA splits a frequency into time slots.
GSM
TDMA is also used as the access technology for Global System for Mobile communications (GSM).
However, GSM implements TDMA in a somewhat different and incompatible way from
IS-136. Think of GSM and IS-136 as two different operating systems that work on
the same processor, like Windows and Linux both working on an Intel Pentium
III. GSM systems use encryption to make phone calls more secure. GSM operates
in the 900-MHz and 1800-MHz bands in Europe and Asia and in the 850-MHz and
1900-MHz (sometimes referred to as 1.9-GHz) band in the United States. It is
used in digital cellular and PCS-based systems. GSM is also the basis for Integrated Digital Enhanced Network (IDEN), a
popular system introduced by Motorola and used by Nextel.
GSM is the international standard in Europe, Australia and much of Asia and Africa. In covered areas, cell-phone users can buy one phone that will work anywhere where the standard is supported. To connect to the specific service providers in these different countries, GSM users simply switch subscriber identification module (SIM) cards. SIM cards are small removable disks/chips that slip in and out of GSM cell phones. They store all the connection data and identification numbers you need to access a particular wireless service provider.
The 850MHz/1900-MHz GSM phones used in the United States are not compatible with the international system. If you live in the United States and need to have cell phone access when you're overseas, you can either buy a tri-band or quad-band GSM phone and use it both at home and when traveling or just buy a GSM 900MHz/1800MHz cell phone for traveling
GSM is the international standard in Europe, Australia and much of Asia and Africa. In covered areas, cell-phone users can buy one phone that will work anywhere where the standard is supported. To connect to the specific service providers in these different countries, GSM users simply switch subscriber identification module (SIM) cards. SIM cards are small removable disks/chips that slip in and out of GSM cell phones. They store all the connection data and identification numbers you need to access a particular wireless service provider.
The 850MHz/1900-MHz GSM phones used in the United States are not compatible with the international system. If you live in the United States and need to have cell phone access when you're overseas, you can either buy a tri-band or quad-band GSM phone and use it both at home and when traveling or just buy a GSM 900MHz/1800MHz cell phone for traveling
Unlocking Your GSM Phone
Any GSM phone can work with any SIM card, but some service providers "lock" the phone so that it will only work with their service. If your phone is locked, you can't use it with any other service provider, whether locally or overseas. You can unlock the phone using a special code -- but it's unlikely your service provider will give it to you. There are Web sites that will give you the unlock code, some for a small fee, some for free.
Any GSM phone can work with any SIM card, but some service providers "lock" the phone so that it will only work with their service. If your phone is locked, you can't use it with any other service provider, whether locally or overseas. You can unlock the phone using a special code -- but it's unlikely your service provider will give it to you. There are Web sites that will give you the unlock code, some for a small fee, some for free.
CDMA
CDMA takes an entirely different approach from TDMA. CDMA,
after digitizing data, spreads it out over the entire available bandwidth.
Multiple calls are overlaid on each other on the channel, with each assigned a
unique sequence code. CDMA is a form of spread spectrum, which simply means
that data is sent in small pieces over a number of the discrete frequencies
available for use at any time in the specified range.
In CDMA, each phone's data has a unique code.
All of the users transmit in the same wide-band chunk of the spectrum. Each user's signal is spread over the entire bandwidth by a unique spreading code. At the receiver’s end, that same unique code is used to recover the signal. Since CDMA systems need to put an accurate time-stamp on each piece of a signal, they reference the GPS system for this information. Between eight and 10 separate calls can be carried in the same channel space as one analog AMPS call. CDMA technology is the basis for Interim Standard 95 (IS-95) and operates in both the 800-MHz and 1900-MHz frequency bands.
Generally, TDMA and CDMA are transparent to each other. In practice, high-power CDMA signals raise the noise floor for TDMA receivers, and high-power TDMA signals can cause overloading and jamming of CDMA receivers.
2G is a cell phone network protocol.
Now let's look at the distinction between multiple-band and multiple-mode technologies.
In CDMA, each phone's data has a unique code.
All of the users transmit in the same wide-band chunk of the spectrum. Each user's signal is spread over the entire bandwidth by a unique spreading code. At the receiver’s end, that same unique code is used to recover the signal. Since CDMA systems need to put an accurate time-stamp on each piece of a signal, they reference the GPS system for this information. Between eight and 10 separate calls can be carried in the same channel space as one analog AMPS call. CDMA technology is the basis for Interim Standard 95 (IS-95) and operates in both the 800-MHz and 1900-MHz frequency bands.
Generally, TDMA and CDMA are transparent to each other. In practice, high-power CDMA signals raise the noise floor for TDMA receivers, and high-power TDMA signals can cause overloading and jamming of CDMA receivers.
2G is a cell phone network protocol.
Now let's look at the distinction between multiple-band and multiple-mode technologies.
Multi-band vs. Multi-mode Cell
Phones
Dual Band vs. Dual Mode
If you travel a lot, you will probably want to look for phones that offer multiple bands, multiple modes, or both. Let's take a look at each of these options:
* Multiple band - A phone that has multiple-band capability can switch frequencies. For example, a dual-band TDMA phone could use TDMA services in either an 800-MHz or a 1900-MHz system. A quad-band GSM phone could use GSM service in the 850-MHz, 900-MHz, 1800-MHz or 1900-MHz band.
* Multiple mode - In cell phones, "mode" refers to the type of transmission technology used. So, a phone that supported AMPS and TDMA could switch back and forth as needed. It is important that one of the modes is AMPS since this gives you analog service if you are in an area that doesn't have digital support.
* Multiple band/Multiple mode - The best of both worlds allows you to switch between frequency bands and transmission modes as needed.
Cellular vs. PCS
Personal Communications Services (PCS) is a wireless phone
service very similar to cellular phone service, but with an emphasis on
personal service and extended mobility. The term "PCS" is often used
in place of "digital cellular," but true PCS means that other
services like paging, caller ID and e-mail are bundled into the service.
While cellular technology was originally created for use in cars, PCS was designed from the ground up for greater user mobility. PCS has smaller cells and therefore requires a larger number of antennas to cover a geographic area. PCS phones use frequencies between 1.85 and 1.99 GHz (1850 MHz to 1990 MHz).
Technically, cellular systems in the United States operate in the 824-MHz to 894-MHz frequency bands; PCS operates in the 1850-MHz to 1990-MHz bands. And while it is based on TDMA, PCS has 200-kHz channel spacing and eight time slots instead of the typical 30-kHz channel spacing and three time slots found in digital cellular.
Changing bands or modes is done automatically by phones that support these options. Ideally the phone will have a default option set, such as 1900-MHz TDMA, and will try to connect at that frequency with that technology first. If it supports dual bands, it will switch to 800 MHz if it cannot connect at 1900 MHz. And if the phone supports more than one mode, it will try the digital mode(s) first, then switch to analog.
You can find both dual-mode and tri-mode phones. The term "tri-mode" can be deceptive. It may mean that the phone supports two digital technologies, such as CDMA and TDMA, as well as analog. In that case, it is a true tri-mode phone. However, it may also mean that it supports one digital technology in two bands and also offers analog support.
While cellular technology was originally created for use in cars, PCS was designed from the ground up for greater user mobility. PCS has smaller cells and therefore requires a larger number of antennas to cover a geographic area. PCS phones use frequencies between 1.85 and 1.99 GHz (1850 MHz to 1990 MHz).
Technically, cellular systems in the United States operate in the 824-MHz to 894-MHz frequency bands; PCS operates in the 1850-MHz to 1990-MHz bands. And while it is based on TDMA, PCS has 200-kHz channel spacing and eight time slots instead of the typical 30-kHz channel spacing and three time slots found in digital cellular.
Changing bands or modes is done automatically by phones that support these options. Ideally the phone will have a default option set, such as 1900-MHz TDMA, and will try to connect at that frequency with that technology first. If it supports dual bands, it will switch to 800 MHz if it cannot connect at 1900 MHz. And if the phone supports more than one mode, it will try the digital mode(s) first, then switch to analog.
You can find both dual-mode and tri-mode phones. The term "tri-mode" can be deceptive. It may mean that the phone supports two digital technologies, such as CDMA and TDMA, as well as analog. In that case, it is a true tri-mode phone. However, it may also mean that it supports one digital technology in two bands and also offers analog support.
A popular version of the tri-mode type of phone for people
who do a lot of international traveling has GSM service in the 900-MHz band for
Europe and Asia and the 1900-MHz band for the United States, in addition to the
analog service. Technically, this is a dual-mode phone, and one of those modes
(GSM) supports two bands.
3G and 3GS Technology
Now, let’s
take a look at 3G mobile-phone technology.
3G technology is the latest in mobile communications. 3G stands for "third generation" - this makes analog cellular technology generation one and digital/PCS generation two. 3G technology is intended for the true multimedia cell phone - typically called smart phones - and features increased bandwidth and transfer rates to accommodate web-based applications and phone-based audio and video files.
3G comprises several cellular access technologies. The three most common ones as of 2005 are:
* CDMA2000 - based on 2G Code Division Multiple Access (see Cellular Access Technologies)
* WCDMA (UMTS) - Wideband Code Division Multiple Access
* TD-SCDMA - Time-division Synchronous Code-division Multiple Access
3G technology is the latest in mobile communications. 3G stands for "third generation" - this makes analog cellular technology generation one and digital/PCS generation two. 3G technology is intended for the true multimedia cell phone - typically called smart phones - and features increased bandwidth and transfer rates to accommodate web-based applications and phone-based audio and video files.
3G comprises several cellular access technologies. The three most common ones as of 2005 are:
* CDMA2000 - based on 2G Code Division Multiple Access (see Cellular Access Technologies)
* WCDMA (UMTS) - Wideband Code Division Multiple Access
* TD-SCDMA - Time-division Synchronous Code-division Multiple Access
3G
networks have potential transfer
speeds of up to 3 Mbps (about 15 seconds to download a 3-minute MP3 song). For
comparison, the fastest 2G phones can achieve up to 144Kbps (about 8 minutes to
download a 3-minute song). 3G's high data rates are ideal for downloading
information from the Internet and sending and receiving large, multimedia
files. 3G phones are like mini-laptops and can accommodate broadband
applications like video conferencing, receiving streaming video from the Web,
sending and receiving faxes and instantly downloading e-mail messages with
attachments.
3GS feels wonderfully familiar – it’s design is almost identical to the 3G, and it’s not until you switch the device on that you start to appreciate the differences. The “S” stands for speed – Apple has used a faster processor in the 3GS, and the effect is immediate, with applications loading more briskly, programs running noticeably faster, and the already slick user-interface getting an extra layer of go-faster stripes. It is also HSDPA-compatible, a step up from 3G, meaning it can surf the web at faster speeds. Battery life is longer, too.
3GS feels wonderfully familiar – it’s design is almost identical to the 3G, and it’s not until you switch the device on that you start to appreciate the differences. The “S” stands for speed – Apple has used a faster processor in the 3GS, and the effect is immediate, with applications loading more briskly, programs running noticeably faster, and the already slick user-interface getting an extra layer of go-faster stripes. It is also HSDPA-compatible, a step up from 3G, meaning it can surf the web at faster speeds. Battery life is longer, too.
Credits:
cellphonerepairtutorials.blogspot.com
cellphonerepairtutorials.blogspot.com